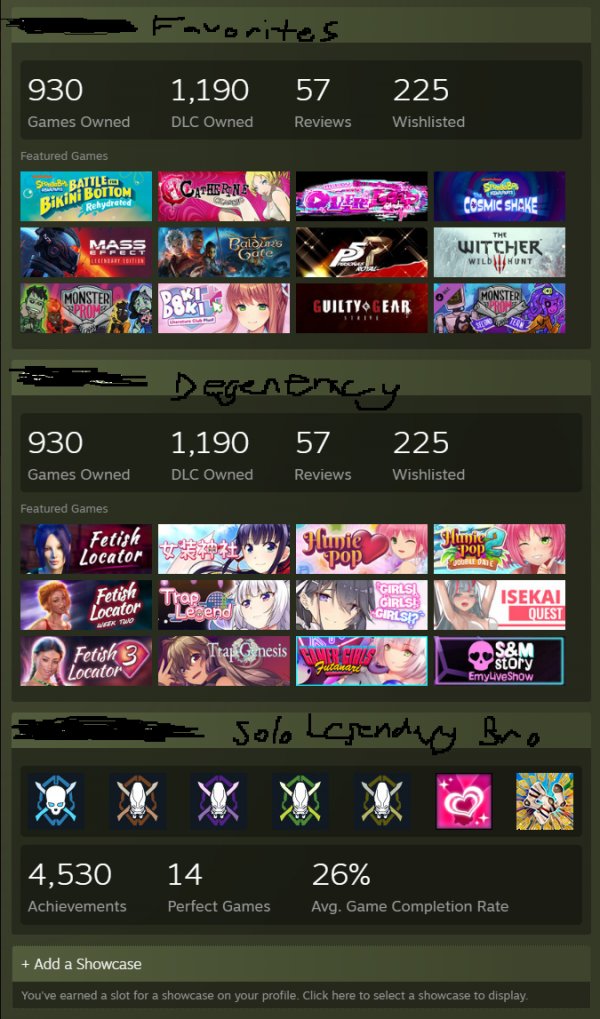
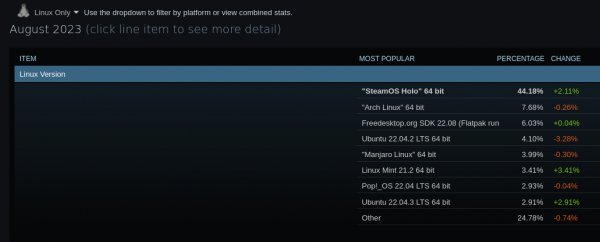
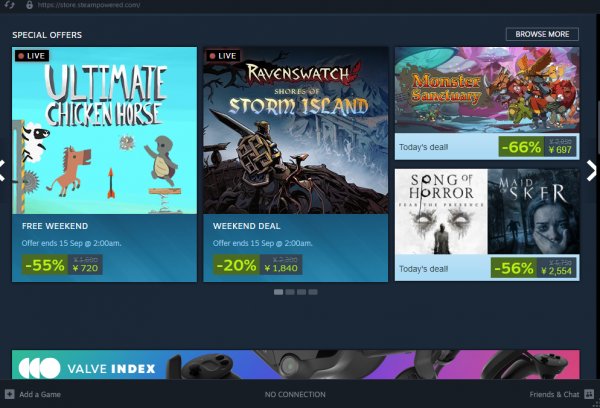
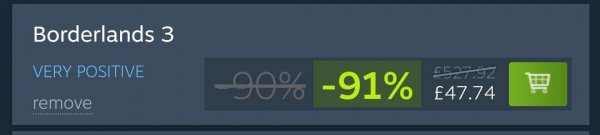
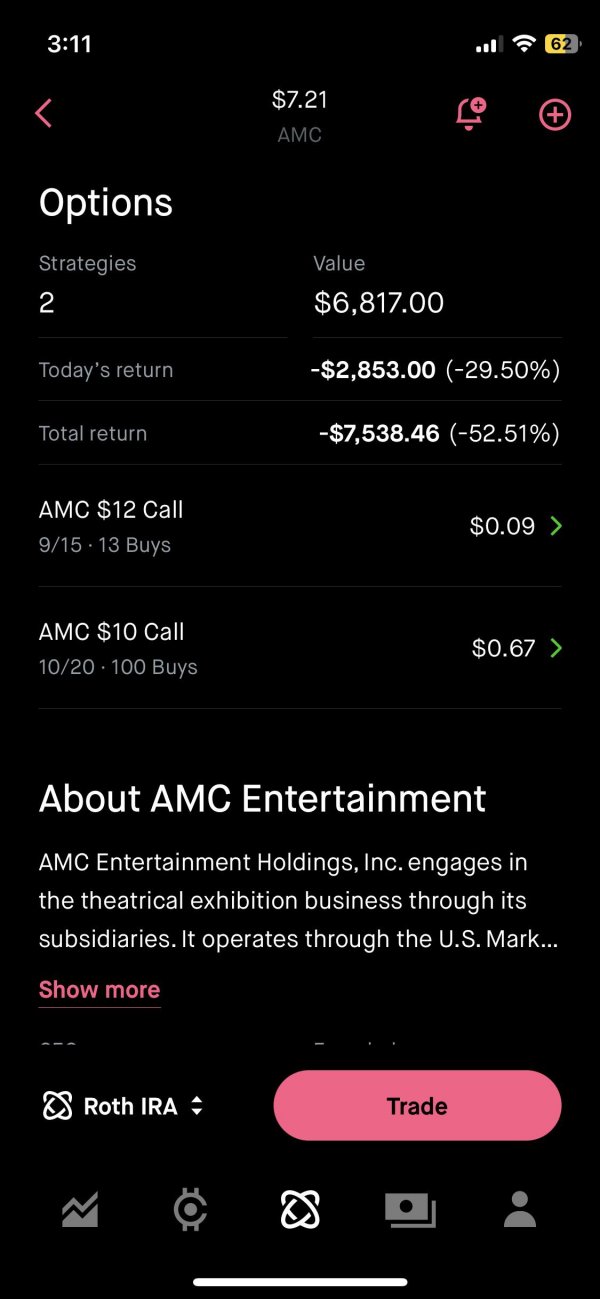
Joint Chiefs: Halo's High Command
List of terpenes:
1. Limonene: Limonene is a citrus-scented terpene known for its uplifting and mood-enhancing properties, and it may also have potential anti-anxiety and anti-depressant effects.
2. Myrcene: Myrcene is an earthy, musky terpene that is often associated with relaxing and sedative effects, making it a common component in indica strains.
3. Pinene: As the name suggests, pinene carries a distinct pine aroma and is believed to have anti-inflammatory properties, making it potentially beneficial for respiratory health.
4. Linalool: Linalool is a floral and lavender-scented terpene known for its calming and stress-relieving effects, often sought after for its potential to aid with anxiety and sleep disorders.
5. Humulene: With an earthy, woody aroma, humulene is thought to have appetite-suppressant and anti-inflammatory properties, making it of interest in wellness and health applications.
6. Caryophyllene: This terpene emits a spicy, peppery scent and is unique among terpenes as it can also interact with CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system, potentially offering anti-inflammatory benefits.
7. Ocimene: Ocimene has a sweet, citrusy, and herbal scent and is believed to possess anti-fungal, anti-bacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
8. Terpinolene: Offering a fresh, sweet, and herbal aroma, terpinolene is known for its antioxidant and potentially sedative effects.
9. Eucalyptol: This terpene carries a refreshing, minty scent similar to eucalyptus and is believed to have potential anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator properties.
10. Geraniol: With a floral, rose-like scent, geraniol is considered to have potential anti-anxiety, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects.
These terpenes, in combination with cannabinoids, contribute to the unique effects and characteristics of different cannabis strains.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a crucial regulatory system in the human body that plays a fundamental role in maintaining homeostasis, or balance, across various physiological functions. Comprising receptors, endocannabinoids (naturally occurring cannabinoids produced within the body), and enzymes, the ECS is distributed throughout the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. When activated, this system influences processes such as pain perception, immune response, mood regulation, and more.
Cannabinoids, on the other hand, are chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant. They can interact with the ECS by binding to its receptors, mimicking the effects of endocannabinoids. This interaction can lead to a wide range of therapeutic effects. In contrast, terpenes are aromatic compounds found in various plants, including cannabis. They contribute to the distinct aroma and flavor of different cannabis strains. Terpenes have their own set of potential therapeutic properties, which can complement the effects of cannabinoids, but they do not directly interact with the ECS like cannabinoids do. Together, cannabinoids and terpenes work synergistically to produce the varying effects of different cannabis strains.